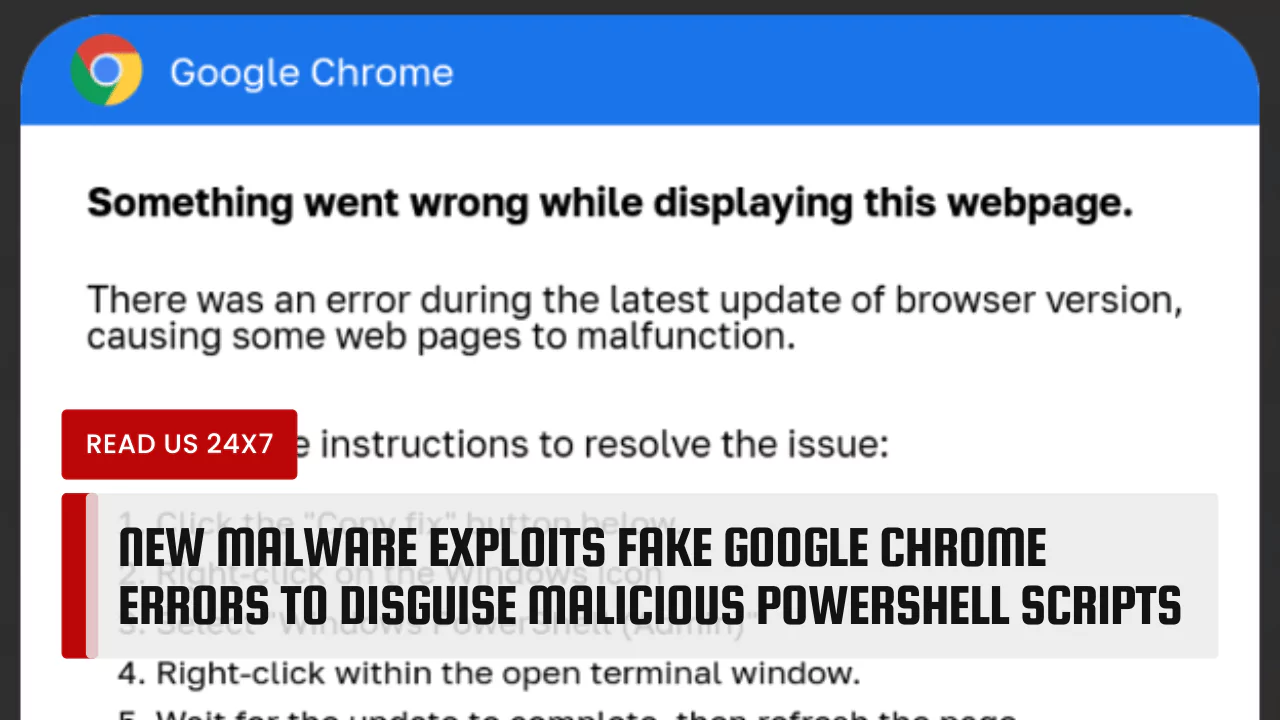
A recently discovered malware distribution effort is utilizing deceptive tactics by exploiting bogus faults in popular software such as Google Chrome, Word, and OneDrive. The campaign tricks users into executing malicious PowerShell “fixes” that ultimately install malware on their systems.
Malicious Distribution Campaign Using Fake Google Chrome Errors
The latest malware strategy involves the utilization of deceptive overlays displaying fake Google Chrome, Microsoft Word, and OneDrive errors. These fraudulent errors prompt users to click a button to copy a PowerShell “fix” into the clipboard and subsequently run it in a Run: dialog or PowerShell prompt, resulting in the installation of malware. The campaign involves multiple threat actors, including ClearFake, ClickFix, and the TA571 threat actor, known for operating as a spam distributor that leads to malware and ransomware infections.
How the Attack Works
The attack chain requires significant user interaction, with the social engineering tactics proving to be particularly deceptive. The fake Google Chrome, Word, and OneDrive errors are ingeniously designed to present a seemingly genuine problem and solution, prompting users to take action without adequately considering the potential risk. The instructions to run the PowerShell script are seamlessly integrated within the fake error messages, creating a convincing facade.
Prevention and Protection Measures
To mitigate the risk posed by such deceptive tactics, users are advised to exercise caution when handling emails and messages. It is essential to remain vigilant and wary of suspicious communications, especially those prompting the execution of unfamiliar scripts or commands. Additionally, maintaining up-to-date security software and operating system ensures the capability to detect and combat evolving threats. Implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, strengthening defenses against unauthorized access and potential malware installation.