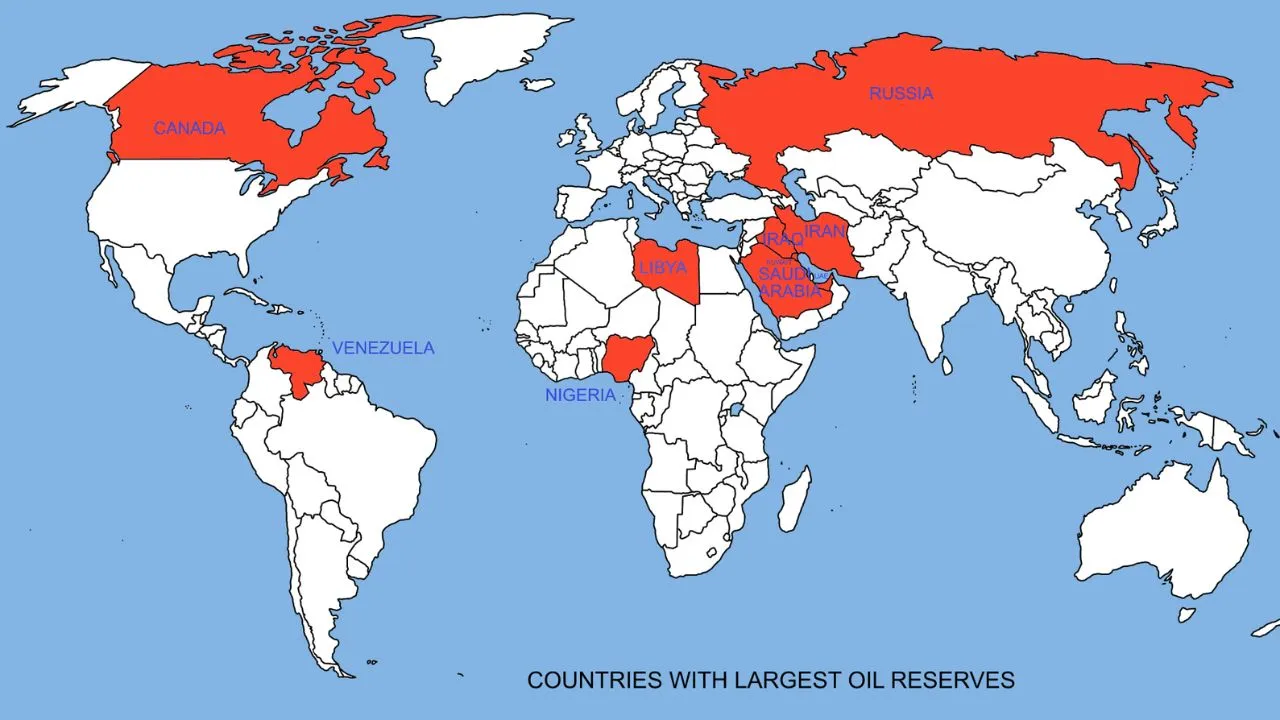
Millions of years ago, the Middle East was predominantly submerged under the Tethys Ocean, which is the primary reason behind its large oil reserves.
The Tethys Ocean received essential nutrients from rivers that flowed into it, fostering a thriving community of microscopic organisms and marine life.
As these organisms perished, their remains settled on the ocean floor and became enveloped by sediment and salt layers.
Gradually, the combination of heat and pressure underwent a transformative process, converting the organic matter into oil and natural gas.
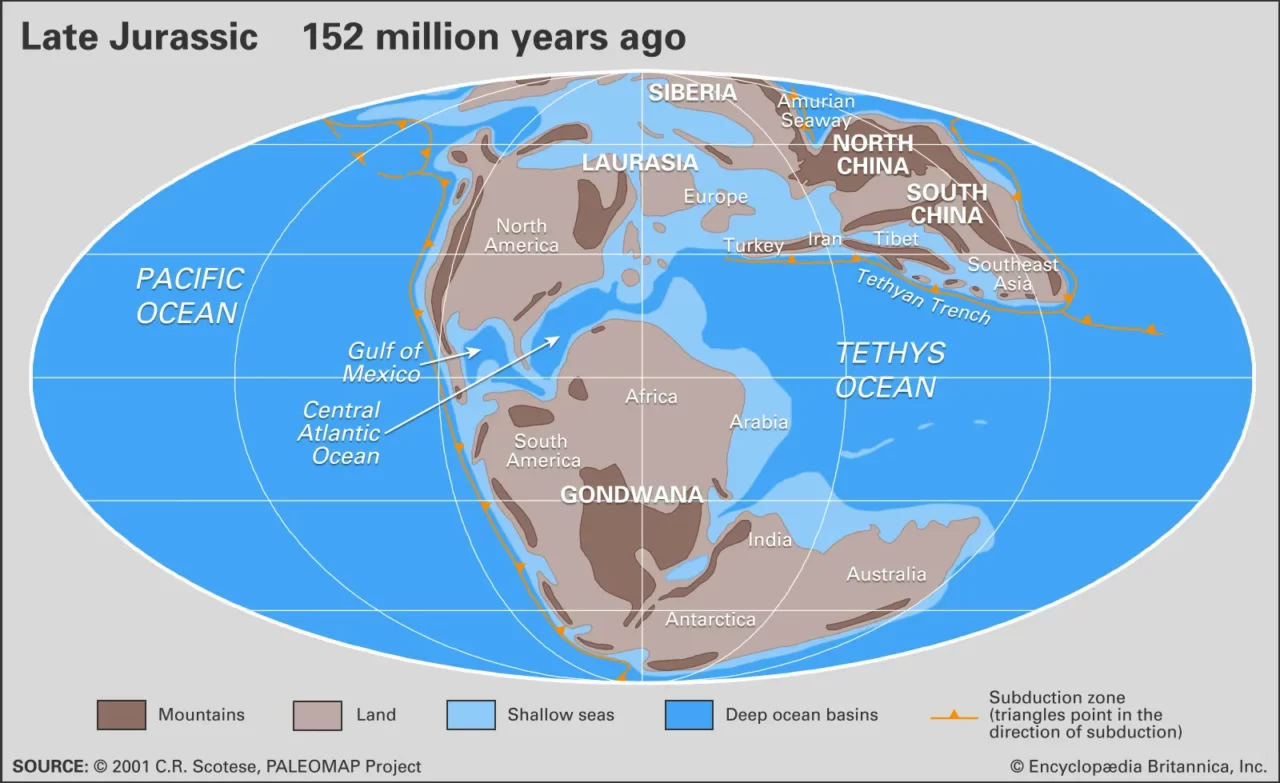
These valuable resources became confined within porous rocks beneath the seabed and subsequently migrated to the land when the Tethys Ocean regressed due to tectonic movements.
This article will take you on a journey through time and space to unravel the reasons behind the Middle East’s oil abundance.
The Geology Behind the Abundance of Oil in the Middle East
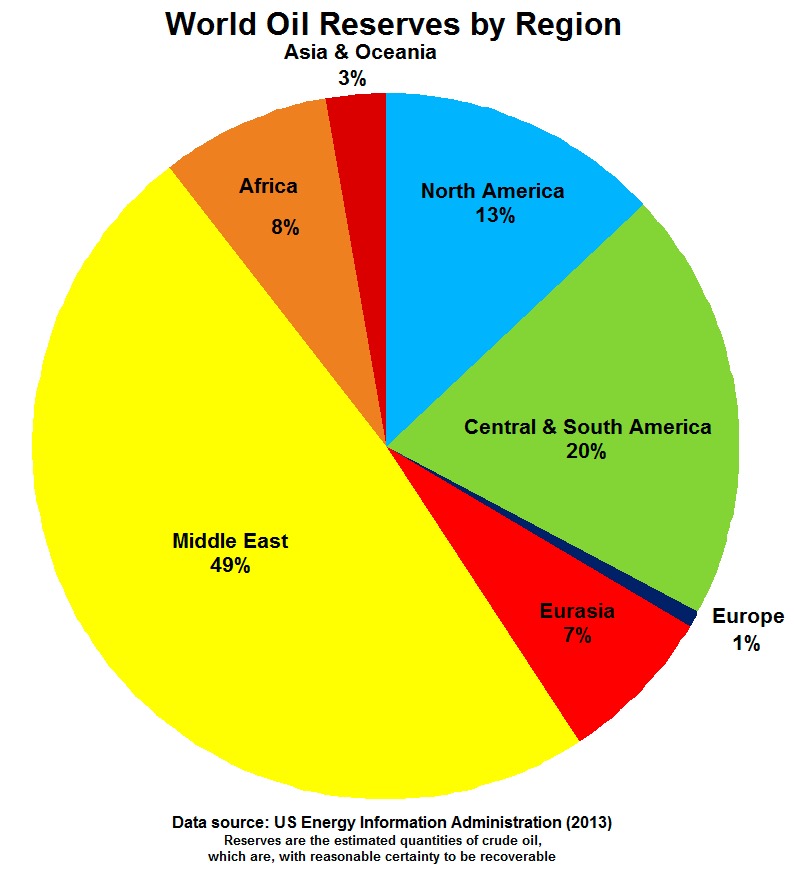
Ancient Sea Beds and Sedimentary Rocks
The Middle East’s oil wealth is largely due to its unique geological history.
Millions of years ago, the region was covered by a shallow sea teeming with microscopic organisms.
When these organisms died, they sank to the sea floor and were buried under layers of sediment.
Over time, heat and pressure transformed these organic materials into oil and gas, which were then trapped in the porous layers of sedimentary rock.
Tectonic Activity and Folding
The Middle East’s geological story doesn’t end there. Tectonic activity played a crucial role in shaping the region’s oil reserves.
The movement of the Earth’s crust caused the sedimentary rocks to fold and fracture, creating traps where oil and gas could accumulate.
These geological structures, known as anticlines, are common in the Middle East and are prime locations for oil exploration.
Trapping Mechanisms
The final piece of the geological puzzle is the trapping mechanisms that prevent the oil from escaping.
In the Middle East, these are typically layers of impermeable rock that cap the oil reservoirs.
These natural seals, combined with the region’s vast sedimentary basins, have resulted in some of the largest oil fields in the world.
The Role of History and Politics in the Middle East’s Oil Riches
Colonialism and Imperialism
The discovery of oil in the Middle East in the early 20th century had profound implications for the region’s political landscape.
European powers, particularly Britain and France, sought to control the oil resources, leading to a period of colonialism and imperialism.
This era shaped the region’s political boundaries and influenced its future oil policies.
Nationalization of Oil Production
The mid-20th century saw a wave of nationalism sweep across the Middle East, leading to the nationalization of oil production.
Countries like Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq took control of their oil industries, often leading to tensions with foreign oil companies.
This shift allowed Middle Eastern countries to exert greater control over their oil wealth and played a significant role in shaping the global oil market.
Geopolitical Conflicts and Alliances
The Middle East’s oil wealth has also been a source of geopolitical conflict and alliances.
The strategic importance of oil has led to wars, political instability, and the formation of oil cartels like OPEC.
These geopolitical dynamics continue to influence the region’s oil production and global oil prices.
Economic and Technological Factors that Contributed to Middle East’s Oil Wealth
Development of Oil Extraction Techniques
Advancements in oil extraction techniques have played a significant role in unlocking the Middle East’s oil wealth.
From the early days of simple drilling rigs to modern techniques like horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing, these technological innovations have made it possible to extract oil from increasingly complex geological formations.
Investment in Oil Infrastructure
The Middle East’s oil wealth has also been driven by substantial investment in oil infrastructure.
This includes everything from drilling rigs and pipelines to refineries and shipping terminals.
These investments have enabled the region to efficiently extract, process, and transport its oil to global markets.
Growth of Global Demand for Oil
Finally, the Middle East’s oil wealth is inextricably linked to the global demand for oil.
The rise of industrialization, the proliferation of automobiles, and the growth of the aviation industry have all fueled a seemingly insatiable demand for oil.
The Middle East, with its vast reserves and low production costs, has been perfectly positioned to meet this demand.
Implications and Future Outlook for the Middle East as the World’s Oil Tank
Impact of Shifts in Global Energy Policies
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, there is a growing shift towards renewable energy sources.
This shift has significant implications for the Middle East’s oil-dependent economies. While oil is likely to remain a crucial part of the global energy mix for the foreseeable future, the transition to a low-carbon economy could impact the demand for Middle Eastern oil.
Alternatives to Fossil Fuels
The rise of alternatives to fossil fuels, such as electric vehicles and renewable energy sources, also poses challenges for the Middle East’s oil economies. However, it also presents opportunities.
Some Middle Eastern countries, notably the United Arab Emirates, are investing heavily in renewable energy and seeking to position themselves as leaders in the energy transition.
Economic and Societal Consequences for the Middle East
The Middle East’s reliance on oil has both economic and societal consequences. While oil wealth has brought prosperity to some, it has also led to economic inequality and social unrest.
Furthermore, the reliance on oil revenues has often hindered the development of other sectors of the economy, leading to concerns about economic diversification.
Importance of Sustainability and Diversification
The future of the Middle East’s oil wealth will likely hinge on its ability to diversify its economies and embrace sustainability.
This includes investing in renewable energy, developing other sectors of the economy, and addressing social and economic inequalities.
The transition may not be easy, but it is essential for the region’s long-term prosperity.
Conclusion
The Middle East’s oil wealth is a complex tapestry woven from the threads of geology, history, politics, and economics.
From ancient sea beds and tectonic activity to colonialism and global energy demand, a myriad of factors has contributed to the region’s oil abundance.
As the world stands on the cusp of a new energy era, the Middle East faces both challenges and opportunities.
The region’s future will depend on its ability to navigate these shifting sands and chart a course toward a sustainable and diversified future.
So, the next time you fill up your gas tank, spare a thought for the fascinating story behind the Middle East’s oil wealth.