Wireless charging is a convenient and eco-friendly way to power up your devices without using cables or plugs. But what if wireless charging could be even faster, more efficient, and more compatible with different devices? That’s what Qi2, the next generation of the Qi wireless charging standard, aims to achieve.
In this article, we will explore the evolution of Qi wireless charging, the features and benefits of Qi2, and the advancements in Qi2 wireless charging technology.
Evolution of Qi Wireless Charging Standard
What is Qi Wireless Charging?
Qi, pronounced as “chee,” is a wireless charging standard created by the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC). It is an open and collaborative standard that has gained significant popularity in the consumer electronics industry. Currently, Qi technology allows for power transfer of up to 15W to mobile phones and portable gadgets. Currently, there are more than 7,500 varieties of smartphone chargers that have obtained Qi certification, and there are also several Qi certified receivers available in the market. The Qi wireless charging market is projected to achieve sales exceeding one billion units by the conclusion of 2023.
How Does Wireless Charging Work?
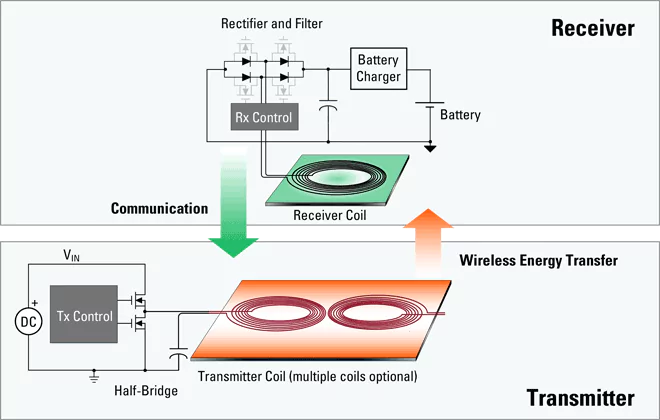
Wireless charging relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Inside every wireless charger, you’ll find a coil of copper wire. When you plug it in, the electric current passing through this coil generates a magnetic field. Meanwhile, devices that support wireless charging include a coil under their back plastic or glass shells. When you place your device on a charging pad, the magnetic field from the charger induces an electric current in the device’s coil. This current then charges the battery of the device.
Evolution of Qi Standards from 2010 to 2021
The WPC introduced Version 1.0 of the Qi wireless charging standard in 2010, which supported single coil, coil arrays, and moving coil designs that allowed transmitters to deliver up to 5W of power. However, Version 1.0 transmitters had limited flexibility. Thus, manufacturers could only optimize the wireless charging process by making adjustments to Qi receiver designs.
In 2012, version 1.1 increased the number of supported transmitter types to 12, giving manufacturers greater flexibility and design freedom. Version 1.1 also introduced the concept of power classes, which defined the maximum power output of a transmitter and the maximum power input of a receiver. The basic power profile (BPP) supported up to 5W, while the extended power profile (EPP) supported up to 15W.
In 2015, version 1.2 added the option of using resonant wireless charging, which increased the distance and spatial freedom between the transmitter and receiver coils. Resonant wireless charging also enabled multi-device charging, where one transmitter could charge multiple receivers simultaneously. However, resonant wireless charging was less efficient and more complex than inductive wireless charging and required additional hardware and software components.
In 2021, the WPC announced the release of version 2.0 of the Qi wireless charging standard, which introduced a new feature called the magnetic power profile (MPP).
Introduction of Qi2 and MPP
The magnetic power profile (MPP) is a technology that is at the core of Qi2, the next generation of the Qi wireless charging standard. MPP technology uses magnets to automatically align the wireless charging transmitter and receiver coils perfectly before wirelessly transferring power. This alignment ensures optimal efficiency, speed, and convenience of wireless charging.
Qi2 devices feature a ring of magnets around the transmitter and receiver coils, which create a strong attraction and a fixed position between them. This eliminates the need to find the “sweet spot” for wireless charging and prevents the device from sliding off the charger. Qi2 devices can also support new product form factors and accessories that magnetically attach to the back of the device, such as cases, wallets, tripods, and cooling fans.
Qi2 devices are backward compatible with Qi devices that support BPP or EPP, meaning that they can charge or be charged by older Qi devices at 5W or 15W, respectively. However, Qi2 devices can only achieve the full benefits of MPP when paired with another Qi2 device, which can deliver up to 15W of power with improved efficiency and safety.
What is Qi2 and How Does It Work?
Protocol Operating Mode of MPP
Qi2 devices use a protocol operating mode called MPP to communicate and negotiate the power transfer between the transmitter and receiver. MPP is based on the existing Qi protocol but with some modifications and enhancements.
MPP uses amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation to send messages from the receiver to the transmitter, and frequency-shift keying (FSK) modulation to send messages from the transmitter to the receiver. ASK and FSK are methods of encoding digital data into analog signals by changing the amplitude or frequency of a carrier wave.
MPP also uses a new message type called MPP Negotiation Request (MPPNR), which is sent by the receiver to initiate the MPP mode. The MPPNR message contains information about the receiver’s capabilities, such as the maximum power input, the coil resistance, and the coil temperature. The transmitter then responds with an MPP Negotiation Response (MPPNS) message, which contains information about the transmitter’s capabilities, such as the maximum power output, the coil resistance, and the coil temperature.
The transmitter and receiver then exchange MPP Power Transfer Request (MPPTR) and MPP Power Transfer Response (MPPRS) messages to establish and maintain the power transfer. The MPPTR and MPPRS messages contain information about the current power level, the voltage, the current, and the frequency of the power transfer.
Differences Between MPP, BPP, EPP
MPP is different from BPP and EPP in several ways. First, MPP requires the presence of magnets in both the transmitter and receiver coils, while BPP and EPP do not. Second, MPP uses a different operating frequency range than BPP and EPP. MPP operates at 110-205 kHz, while BPP and EPP operate at 100-205 kHz. Third, MPP has a different power control algorithm than BPP and EPP. MPP uses a closed-loop power control algorithm, which adjusts the power level based on the feedback from the receiver. BPP and EPP use an open-loop power control algorithm, which adjusts the power level based on the transmitter’s estimation of the receiver’s needs.
Benefits of MPP and Changes in Operating Frequency
MPP offers several benefits over BPP and EPP, such as:
- Faster and more efficient charging: MPP can deliver up to 15W of power with less energy loss and less heat generation, thanks to the perfect alignment of the transmitter and receiver coils. This means that devices can charge faster and last longer.
- Easier and more convenient charging: MPP eliminates the need to find the “sweet spot” for wireless charging, and prevents the device from sliding off the charger. Users can simply place their device on the charger and feel the magnetic click.
- More compatible and interoperable charging: MPP is backward compatible with BPP and EPP devices, meaning that Qi2 devices can charge or be charged by older Qi devices at 5W or 15W, respectively. MPP also supports new product form factors and accessories that magnetically attach to the back of the device, such as cases, wallets, tripods, and cooling fans.
The change in operating frequency range from 100-205 kHz to 110-205 kHz for MPP is due to the presence of magnets in the transmitter and receiver coils. The magnets create a magnetic bias field, which affects the inductance and resonance of the coils. The change in frequency range compensates for this effect and ensures optimal power transfer.
Obtaining Qi2 Certification
Qi2 certification is a process that ensures the quality and safety of Qi2 products and enables them to work with other Qi2 devices. Here are some information about obtaining Qi2 certification:
Requirements for Qi2 Certification
- Compliance with Qi2 standards: Products must meet all the technical specifications outlined in the Qi2 standard. These include power levels, efficiency, safety features, and interoperability.
- Testing by a WPC-authorized test lab: Products must undergo rigorous testing by a WPC-approved lab to ensure they meet the required standards.
- Pre-installation of a unique certificate: All Qi2 power transmitters above 5W must have a unique certificate pre-installed during manufacturing.
- Self-signed Root Certificate Hash: This certificate verifies the authenticity of the Qi2 product and ensures it complies with the standard.
Process of Obtaining Certification
- Contact a WPC-authorized test lab: Identify a lab authorized by the WPC to conduct Qi2 testing.
- Submit your product for testing: Provide the lab with your product samples and all necessary documentation.
- Testing and evaluation: The lab will conduct a series of tests to assess your product’s compliance with the Qi2 standard.
- Certification decision: The WPC will review the test results and issue a certification decision.
- Pre-installation of the certificate: Once certified, manufacturers must pre-install the unique certificate in all Qi2 power transmitters.
- Marketing and promotion: You can now market and promote your product as a certified Qi2 device.
Importance of Qi2 Certification
- Ensures quality and safety: Qi2 certification guarantees that your product meets high standards for quality, performance, and safety.
- Improves brand reputation: Certification shows your commitment to quality and industry standards, enhancing your brand reputation.
- Increases market competitiveness: Consumers are more likely to trust and purchase certified products.
- Enables wider compatibility: Qi2 certification ensures your product is compatible with other Qi2 devices, expanding your market reach.
- Promotes innovation: The Qi2 standard encourages innovation by providing a common platform for device manufacturers to collaborate and develop new technologies.
Advancements in Qi2 Wireless Charging Technology
Interoperability and Compatibility With Various Devices
One of the main advantages of Qi2 wireless charging technology is its interoperability and compatibility with various devices. Qi2 devices are backward compatible with Qi devices that support BPP or EPP, meaning that they can charge or be charged by older Qi devices at 5W or 15W, respectively. Qi2 devices can also support new product form factors and accessories that magnetically attach to the back of the device, such as cases, wallets, tripods, or cooling fans.
Qi2 devices can also communicate and negotiate the power transfer with other Qi2 devices, using the MPP protocol. This allows Qi2 devices to achieve the full benefits of MPP, such as faster and more efficient charging, easier and more convenient charging, and more compatible and interoperable charging.
Qi2 devices can also work with other wireless charging standards, such as the AirFuel Resonant standard, which is another open, collaborative wireless charging standard developed by the AirFuel Alliance. Qi2 devices can detect and switch to the AirFuel Resonant mode, which operates at 6.78 MHz, and can deliver up to 30W of power over a distance of up to 50 mm. This enables Qi2 devices to charge or be charged by AirFuel Resonant devices, such as laptops, tablets, or monitors.
Infineon’s Introduction of the First Qi2 MPP Wireless Charging Transmitter
Infineon Technologies AG, a leading semiconductor company, has introduced the first Qi2 MPP wireless charging transmitter, which is based on its XMC™ microcontroller and AURIX™ microcontroller families. The Infineon Qi2 MPP wireless charging transmitter is designed to provide a fast, efficient, and convenient wireless charging solution for smartphones and other handheld devices.
The Infineon Qi2 MPP wireless charging transmitter features the following characteristics:
- It supports up to 15W of power transfer with MPP, and up to 30W of power transfer with AirFuel Resonant.
- It uses a single-coil design, which reduces the cost and complexity of the transmitter.
- It uses a closed-loop power control algorithm, which adjusts the power level based on the feedback from the receiver.
- It uses a proprietary coil driver, which optimizes the efficiency and performance of the transmitter.
- It uses a smart protection scheme, which prevents overheating, overvoltage, overcurrent, and foreign object detection.
The Infineon Qi2 MPP wireless charging transmitter is expected to be available in the market by the end of 2023.
Future Development Trend of Wireless Charging With Qi2

Wireless charging with Qi2 is expected to become more popular and widespread in the future, as more devices and accessories adopt the Qi2 standard and benefit from its features and advantages. Wireless charging with Qi2 is also expected to enable new use cases and scenarios, such as:
- Wireless charging in public places, such as airports, hotels, cafes, or restaurants, where users can easily and conveniently charge their devices without worrying about finding a plug or a cable.
- Wireless charging in vehicles, such as cars, buses, or trains, where users can securely and reliably charge their devices without affecting the driving or the navigation.
- Wireless charging in smart homes, such as kitchens, living rooms, or bedrooms, where users can seamlessly and intuitively charge their devices without disrupting the aesthetics or the functionality of the furniture or the appliances.
- Wireless charging in wearable devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, or headphones, where users can comfortably and continuously charge their devices without removing them from their wrists or their ears.
Wireless charging with Qi2 is also expected to contribute to sustainability and the environment, as it reduces the need for cables, plugs, and adapters, which can generate electronic waste and carbon emissions. Wireless charging with Qi2 is also expected to improve the battery life and the durability of devices, as it prevents overcharging, undercharging, and physical damage.
How Is Qi2 Different from Qi?
Qi2 is different from Qi in several ways, such as:
- Qi2 uses magnets to automatically align the transmitter and receiver coils, while Qi does not.
- Qi2 uses a different operating frequency range than Qi. Qi2 operates at 110-205 kHz, while Qi operates at 100-205 kHz.
- Qi2 uses a different power control algorithm than Qi. Qi2 uses a closed-loop power control algorithm, while Qi uses an open-loop power control algorithm.
- Qi2 supports new product form factors and accessories that magnetically attach to the back of the device, while Qi does not.
- Qi2 can deliver up to 15W of power with MPP, and up to 30W of power with AirFuel Resonant, while Qi can only deliver up to 15W of power with EPP.
Advantages of Qi2 Wireless Charging Technology
Qi2 wireless charging technology offers several advantages over Qi wireless charging technology, such as:
- Faster and more efficient charging: Qi2 can deliver up to 15W of power with MPP, and up to 30W of power with AirFuel Resonant, with less energy loss and less heat generation, thanks to the perfect alignment of the transmitter and receiver coils. This means that devices can charge faster and last longer.
- Easier and more convenient charging: Qi2 eliminates the need to find the “sweet spot” for wireless charging, and prevents the device from sliding off the charger. Users can simply place their device on the charger and feel the magnetic click.
More compatible and interoperable charging: Qi2 is backward compatible with Qi devices that support BPP or EPP, meaning that Qi2 devices can charge or be charged by older Qi devices at 5W or 15W, respectively. Qi2 also supports new product form factors and accessories that magnetically attach to the back of the device, such as cases, wallets, tripods, or cooling fans. Qi2 also works with other wireless charging standards, such as the AirFuel Resonant standard, which can deliver up to 30W of power over a distance of up to 50 mm.


