Not necessarily. Contact lenses with higher water content are more permeable to oxygen, which can be beneficial for eye health. However, they can also be more prone to drying out, which can make them uncomfortable to wear.
Here is a general guideline for choosing the best water content for you:
- Dry eyes: Choose a contact lens with a low water content (38-55%).
- Normal eyes: Choose a contact lens with a medium water content (55-65%).
- Oily eyes: Choose a contact lens with a high water content (65-78%).
What is the Water Content of a Contact Lens?
The water content of a contact lens is the percentage of water that makes up the lens material. It is usually expressed as a percentage, such as 38% or 75%. The water content of a contact lens influences its thickness, oxygen permeability, and comfort.
- The higher the water content, the thicker the lens tends to be. This is because water molecules occupy more space than other molecules in the lens material. A thicker lens may be more noticeable on the eye and may require more care and cleaning.
- The higher the water content, the lower the oxygen permeability tends to be. This is because water molecules block the passage of oxygen through the lens material. Oxygen permeability is a measure of how much oxygen can reach the cornea through the lens. It is expressed as Dk/t, which takes into account both the oxygen permeability (Dk) and the thickness (t) of the lens. A lower oxygen permeability may increase the risk of hypoxia, which is a condition where the cornea does not receive enough oxygen and becomes swollen, irritated, or infected.
- The higher the water content, the more comfortable the lens may feel initially. This is because water molecules make the lens softer and more flexible, which may reduce friction and irritation on the eye. However, comfort may also depend on other factors, such as lens fit, material, and surface properties.
How Much Water Do Contact Lenses Contain?
Contact lenses can be classified into three categories based on their water content: high, mid, and low.
- Low water content (38-40%): Good for people with dry eyes or who live in dry climates.
- Medium water content (41-60%): Good for most contact lens wearers.
- High water content (61-75%): Good for people who wear contact lenses for long periods of time or who have difficulty wearing lower water content contact lenses.
Pros and Cons of High Water Content Lenses
High water content lenses have some benefits and drawbacks that should be considered before choosing them.
Benefits of higher water content lenses include:
- They may feel more comfortable initially, as they are softer and more flexible than lower water content lenses.
- They may be easier to insert and remove, as they are thicker and less likely to fold or tear than lower water content lenses.
- They may be more suitable for people with dry eyes, as they retain more moisture than lower water content lenses.
Drawbacks of higher water content lenses include:
- They may have lower oxygen permeability than lower water content lenses, which may increase the risk of hypoxia and related complications.
- They may dehydrate faster than lower water content lenses, especially in dry or windy environments or when using digital devices for long periods. This may reduce comfort and clarity over time.
- They may require more care and cleaning than lower water content lenses, as they are more prone to deposits and bacteria growth than lower water content lenses.
Water and Oxygen Permeability in Contact Lenses
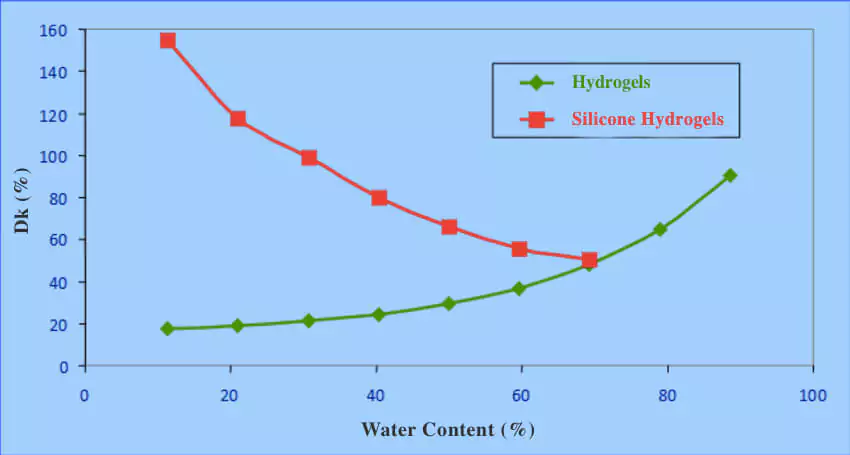
Water and oxygen permeability are two important factors that affect the health and comfort of contact lens wearers. As mentioned earlier, higher water content usually means lower oxygen permeability in contact lenses. However, this is not always the case, as some newer contact lens materials have overcome this trade-off by using silicone hydrogel technology.
Silicone hydrogel materials are soft plastics that contain silicone molecules that allow more oxygen to pass through the lens material regardless of its water content. Silicone hydrogel lenses have higher oxygen permeability than conventional hydrogel lenses with similar or even higher water content. For example, Acuvue Oasys has a water content of 38% and an oxygen permeability of 147 Dk/t, while Acuvue 2 has a water content of 58% and an oxygen permeability of 25.5 Dk/t.
Silicone hydrogel lenses are considered the most advanced and healthy contact lens materials available today, as they provide more oxygen to the cornea and reduce the risk of hypoxia and related complications. However, silicone hydrogel lenses may also have some disadvantages, such as being more expensive, stiffer, or less compatible with some contact lens solutions than conventional hydrogel lenses.
Some popular contact lens brands and their water and oxygen permeability are listed below:
| Brand | Material | Water Content | Oxygen Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acuvue Oasys | Senofilcon A (silicone hydrogel) | 38% | 147 Dk/t |
| Acuvue 2 | Etafilcon A (hydrogel) | 58% | 25.5 Dk/t |
| Air Optix Aqua | Lotrafilcon B (silicone hydrogel) | 33% | 138 Dk/t |
| Biofinity | Comfilcon A (silicone hydrogel) | 48% | 160 Dk/t |
| PureVision 2 | Balafilcon A (silicone hydrogel) | 36% | 130 Dk/t |
| Proclear | Omafilcon A (hydrogel) | 62% | 28 Dk/t |
| Dailies Total 1 | Delefilcon A (silicone hydrogel) | 33% (core), >80% (surface) | 156 Dk/t |
| Bausch & Lomb Ultra | Samfilcon A (silicone hydrogel) | 46% | 163 Dk/t |
Factors to Consider for Comfortable Contact Lenses
Water content is not the only factor that affects the comfort of contact lenses. Other factors that should be considered include:
- Oxygen permeability: As discussed earlier, oxygen permeability is a measure of how much oxygen can reach the cornea through the lens. Higher oxygen permeability means more oxygen and less hypoxia, which may improve comfort and health.
- Lens material: The type of plastic used to make the lens may influence its comfort, as different materials have different properties, such as stiffness, wetting angle, surface smoothness, deposit resistance, and biocompatibility. For example, silicone hydrogel materials are stiffer but more breathable than hydrogel materials, while hydrogel materials are softer but less breathable than silicone hydrogel materials.
- Other considerations: Besides water content, oxygen permeability, and lens material, other factors that may affect comfort include lens fit, design, replacement schedule, wearing time, cleaning regimen, eye health, environmental conditions, and personal preferences. For example, some people may prefer daily disposable lenses over monthly lenses for convenience and hygiene reasons, while others may prefer monthly lenses over daily lenses for cost and environmental reasons.
Why Does Water Content Matter?
Water content is one of the factors that determines the characteristics and performance of contact lenses. It affects the thickness, oxygen permeability, and comfort of the lens. Higher water content lenses may be more comfortable initially, but they may also have lower oxygen permeability and faster dehydration than lower water content lenses. Lower water content lenses may be less comfortable initially, but they may also have higher oxygen permeability and slower dehydration than higher water content lenses.
Water content is not the only factor that matters for contact lens wearers. Other factors such as oxygen permeability, lens material, and other considerations should also be taken into account when choosing contact lenses. The best contact lenses for dry eyes are those that provide enough oxygen and moisture to the cornea while minimizing friction and irritation. The best way to find out which contact lenses are suitable for your eyes is to consult your eye care professional and try different options until you find the most comfortable ones for you.


