Exchange database (EDB) files store the users’ mailboxes containing critical business data, such as emails, contacts, attachments, notes, tasks, journals, etc. If the EDB file gets damaged or corrupt due to events, such as a malicious attacks, server crashes, missing log files, etc., it can lead to downtime and data loss.
Thus, it’s essential to back up the Exchange EDB files. Backups are even more critical when your organization does not use the Database Availability Group (DAG) set up and relies on a standalone (single) Exchange server.
Regular backup helps restore the Exchange server mailbox database quickly, prevents permanent data loss when a disaster strikes, and ensures resumption of Exchange services with minimum downtime.
In this post, we’ve discussed various methods to backup Exchange EDB files and mailboxes using tools available in the Exchange server.
Methods to Backup Exchange EDB Files
To backup EDB files in Exchange Server 2010, 2013, 2016, or 2019, you can use the Windows Server Backup plugin or export individual mailboxes from the EDB file to PST.
Below we have discussed both methods to backup Exchange EDB files.
Method 1: Backup Exchange EDB using Windows Server Backup
You can use the Windows Server Backup (WSB) to backup EDB files in Exchange 2010 and later versions. The WSB is a preferred method to backup Exchange EDB files as it creates a VSS-based backup at the volume level and truncates the log files automatically, which helps conserve the server storage. Also, restoring an EDB file from a WSB backup is easier and convenient.
However, to backup EDB using WSB, you need Organization Management and Server Management permissions and administrative access to the server. Also, you need to install the Windows Server backup feature.
The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Install Windows Server Backup Feature
To install Windows Server backup on your Exchange server, follow these steps:
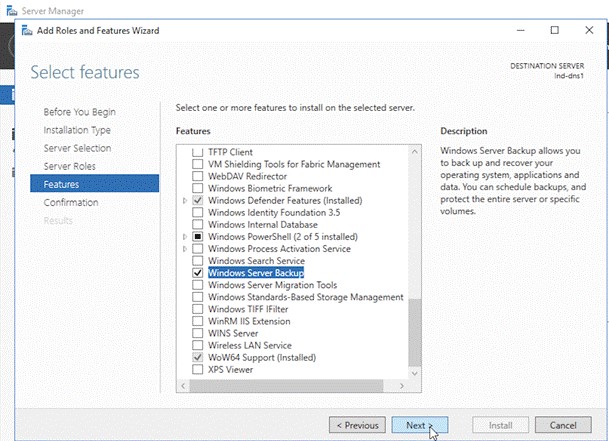
- Open Server Manager and click ‘Add roles and features.’
- Click ‘Installation Type’ and then click ‘Next.’ Then select the server from ‘Server Selection’ and Click ‘’
- Select ‘Windows Server Backup’ from the ‘Features’ list and then click ‘Next.’

- This will install the Windows Server Backup service.
Step 2: Backup Exchange EDB Files
To backup Exchange EDB files using the Windows Server backup, follow these steps:
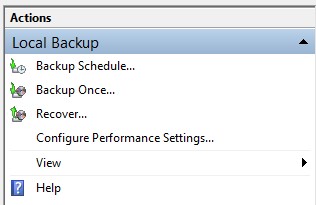
- Open Windows Server Backup service and select Local Backup.

- Select ‘Custom’ and click Next.
- Click Add Items to choose the volume(s) containing the Exchange database (EDB) file, logs files, checkpoint files, and then click
- Click Advanced Settings and go to the Exclusions
- Click Add Exclusion to enter the file types (if any) you don’t want to backup.
- Choose VSS full Backup and click OK > Next.
- Choose local drives to store the backup and click Next. You may also choose the ‘remote shared folder’ to back up to network storage or remote server location.
- Select Backup Destination from the drop-down and click Next. Make sure the destination has enough storage space to store the backup.
- Finally, review the backup settings on the Confirmation page and click Backup.
- The backup will start. You may close the Backup Progress window if you wish. The backup will continue in the background.
To check if the backup was successful, run the following command in the Exchange Management Shell:
Get-MailboxDatabase -Server <ServerName> -Status | Format-List Name,*FullBackup
Method 2: Export Mailboxes from Exchange EDB Files to PST
PST or Personal Storage Table, also known as Personal Folders, is a file format supported by MS Outlook, Exchange, and Office 365. Thus, instead of creating an entire database backup, you can also choose to back up selected individual or multiple mailboxes from an Exchange EDB file to PST.
The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Grant Mailbox Import Export Role
Execute the following cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell to assign the Mailbox Import Export role to the administrator.
New-ManagementRoleAssignment –Role “Mailbox Import Export” –User “administrator”
You may replace “administrator” with your or desired username to assign the Mailbox Import Export role.
Step 2: Export Mailbox from Exchange EDB to PST via Exchange Admin Center
The steps to backup Exchange EDB mailbox as PST are as follows:
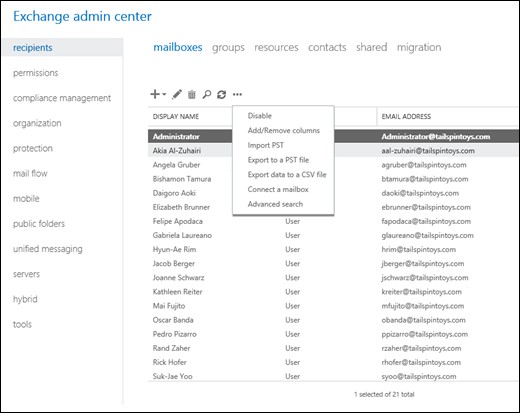
- Open EAC and navigate to Recipients > Mailboxes and click … (more icon).

- Choose ‘Export to a PST file.’

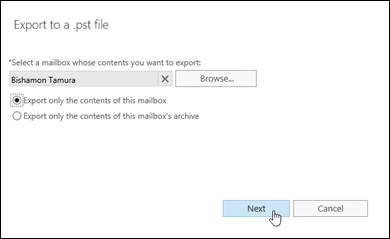
- Click ‘Browse’ to choose a mailbox you want to export and backup from the Exchange EDB file and click ‘Next.’

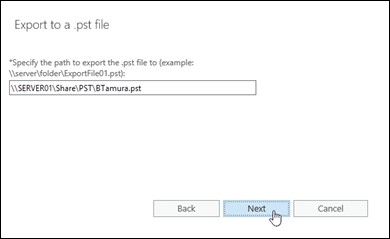
- Enter the UNC path to save the exported mailbox PST file and click ‘Next.’

- Click ‘Browse’ to select users to whom an email will be sent once the export is complete. Click ‘Finish.’
This will export and back up the mailbox from the Exchange EDB file to PST. Next, repeat the steps to back up other mailboxes from the Exchange EDB file. You may also use Exchange Management Shell to create multiple or single mailbox export requests.
Conclusion
Backups are critical, especially when it comes to business data. By maintaining a regular Exchange EDB files backup, you can quickly restore the database and user mailboxes if the database fails or gets dismounted due to inconsistencies or corruption. Backups will save your organization from a data loss situation and help minimize downtime when a disaster strikes. However, you should also verify the backups to ensure that they work as intended.
But if the backups aren’t available or do not work when needed, you can use an Exchange Recovery software, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange. The software helps you repair corrupt or damaged Exchange EDB files and recovers mailboxes to PST files. It can also export the recovered mailboxes from the damaged Exchange database directly to a live Exchange server or Office 365. A highly recommended tool for all your Exchange disaster recovery needs.