Yes, QoS can slow down the internet. This is because QoS works by prioritizing certain types of traffic over others. This means that some traffic may be delayed or even dropped in order to ensure that high-priority traffic flows smoothly.
For example, if you have QoS enabled on your router and you are streaming a video, your router may prioritize the video traffic over other types of traffic, such as web browsing or email. This means that your video may stream more smoothly, but your web browsing or email may be slower.
How much QoS slows down the internet depends on a number of factors, such as your internet connection speed, the types of traffic you are using, and the way you have configured QoS. If you are not careful, you can configure QoS in a way that significantly slows down your internet connection.
However, it is important to note that QoS is not always a bad thing. In fact, it can be very useful for improving the performance of certain applications, such as online gaming or video conferencing. If you are having problems with a particular application, QoS may be able to help.
Understanding Quality of Service (QoS)
Definition of QoS
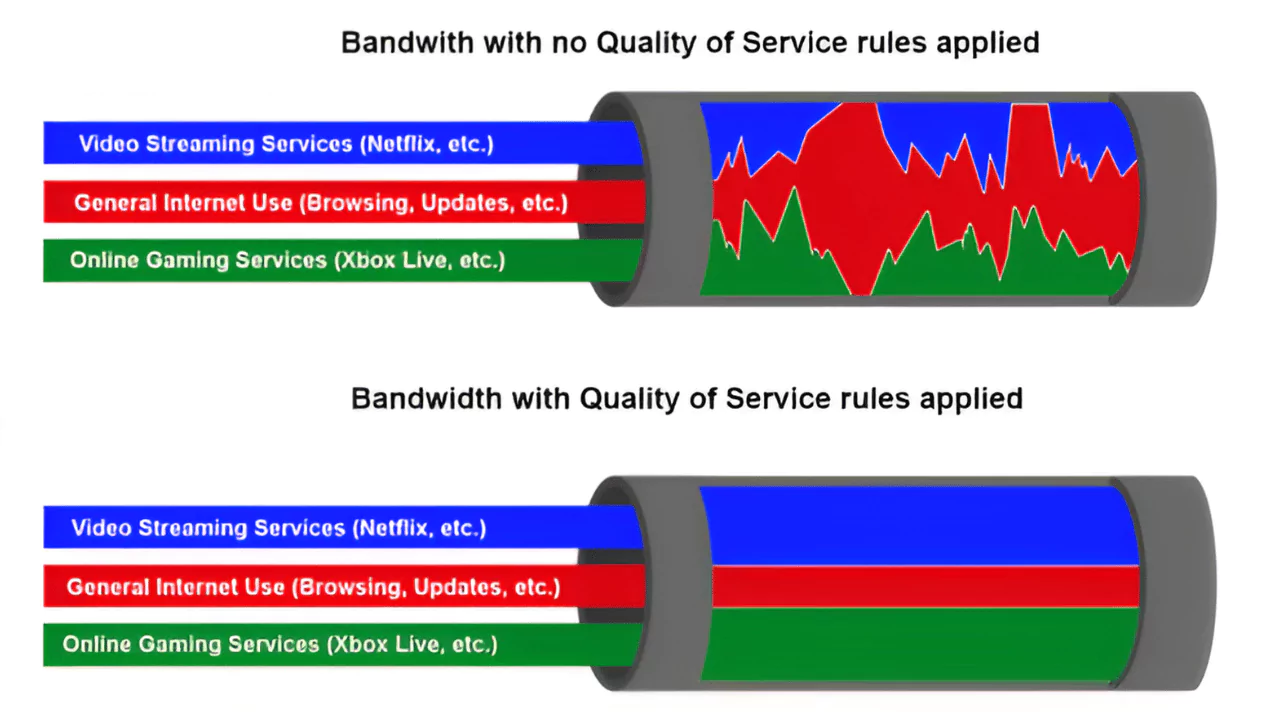
Quality of Service (QoS) is a feature of routers and switches that prioritizes traffic so that more important traffic can pass first. QoS allows network administrators to assign different levels of priority to different types of traffic, such as voice, video, gaming, web browsing, file downloading, etc. QoS can also allocate bandwidth to specific devices or applications, ensuring that they get enough resources to function properly.
Purpose of QoS
The main purpose of QoS is to improve the network performance and user experience by reducing latency, jitter, packet loss, and congestion. QoS is especially useful when the network bandwidth is limited and different demands compete for bandwidth. For example, QoS can help prevent a streaming video from buffering or a Skype call from dropping due to a large file download in the background. QoS can also help optimize network utilization and efficiency by distributing the available bandwidth according to the traffic needs.
How QoS Can Affect Internet Speed?
QoS can have both positive and negative effects on Internet speed, depending on how it is configured and applied. Here are some ways that QoS can influence the Internet speed:
Overhead Cap
Some types of QoS require adding extra information or headers to the packets to indicate their priority or class. This can increase the packet size and reduce the effective bandwidth. For example, if the original packet size is 1500 bytes and the QoS header adds 20 bytes, then the effective bandwidth is reduced by 1.3%. This may not seem significant, but it can add up over time and affect the overall throughput.
Lower Bandwidth
Some types of QoS require setting a lower limit or cap on the bandwidth for certain traffic or devices. This can prevent them from using more than their allocated share of bandwidth, even if there is spare capacity in the network. For example, if a device is assigned 10 Mbps of bandwidth by QoS, it cannot use more than that even if the network has 100 Mbps of bandwidth available. This can limit the maximum speed that the device can achieve.
Network Prioritization
Some types of QoS require prioritizing certain traffic or devices over others based on their importance or urgency. This can improve the speed and quality of service for high-priority traffic or devices at the expense of low-priority ones. For example, if a router has QoS enabled and receives two packets at the same time, one from a streaming video and one from a file download, it will send the video packet first and delay or drop the download packet. This can enhance the video quality but slow down the download speed.
The Debate: Does QoS Actually Slow Down the Internet?
There is no definitive answer to whether QoS slows down or speeds up the Internet, as it depends on various factors that can vary from case to case. Some of these factors are:
- The type of QoS: Different types of QoS have different methods and mechanisms for managing traffic. Some are more complex and sophisticated than others, and some may introduce more overhead or limitations than others.
- The network configuration: Different networks have different architectures and settings that can affect how QoS works. Some networks may have more routers or switches that support QoS than others, and some may have more fine-tuned or customized QoS rules than others.
- The bandwidth availability: Different networks have different amounts of bandwidth that can accommodate different levels of traffic demand. Some networks may have more than enough bandwidth for all traffic without needing QoS, while others may have limited bandwidth that requires QoS to optimize its usage.
- The traffic demand: Different networks have different types and volumes of traffic that compete for bandwidth. Some networks may have more diverse and dynamic traffic than others, and some may have more critical and sensitive traffic than others.
Given these factors, it is possible that QoS can have different outcomes for different networks and scenarios. For some networks, QoS may improve the Internet performance by ensuring that important traffic gets enough bandwidth and quality. For others, QoS may degrade the Internet performance by adding overhead or restricting bandwidth for certain traffic or devices.
Therefore, whether QoS slows down or speeds up the Internet depends on how it is implemented and used in each network context. There is no one-size-fits-all solution or answer to this question. The best way to determine if QoS is beneficial or detrimental to your network is to test it yourself with your own equipment and applications. You may find that QoS can make a difference in your network performance and user experience.