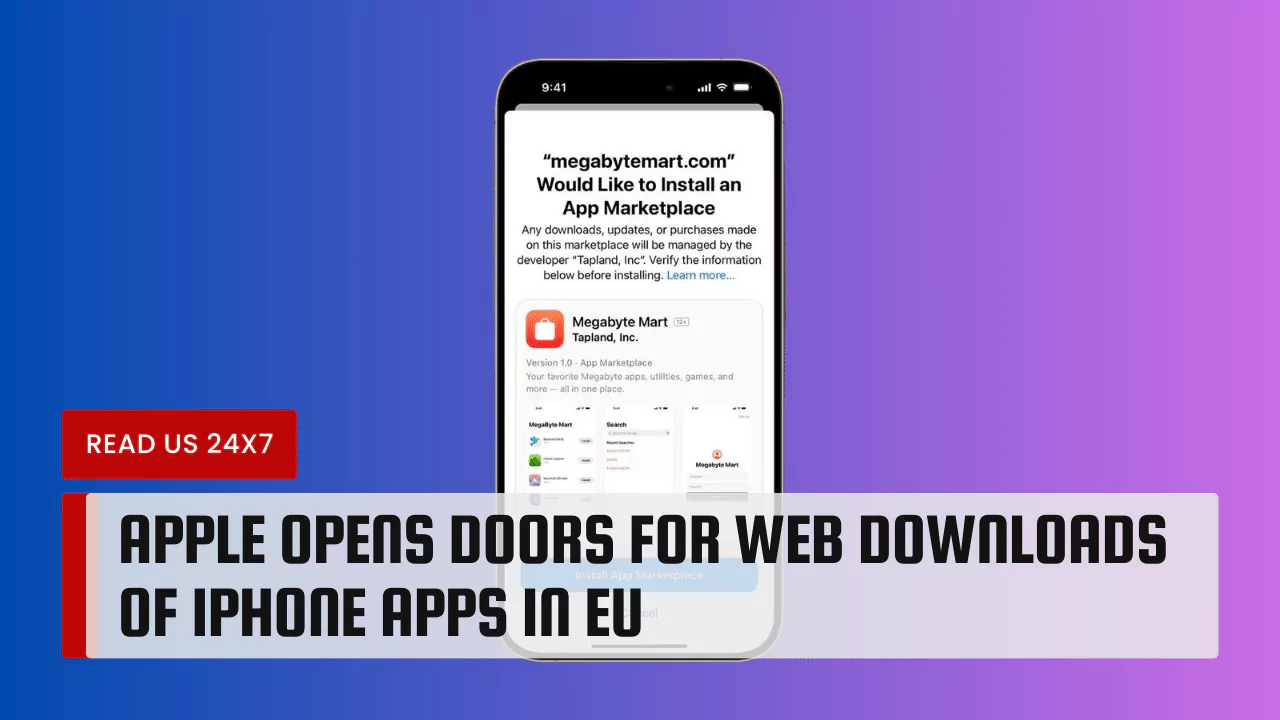
Apple announced a significant shift in its App Store policies for the European Union. The tech giant will allow iPhone users in the EU to download apps directly from websites, a move forced by the European Commission’s Digital Markets Act (DMA). This decision marks a significant departure from Apple’s long-standing resistance to web downloads or “sideloading” of iPhone software.
Changes to Apple’s App Store in the EU
Allowing Third-Party App Downloads from Websites
Under the new policy, developers meeting specific criteria, such as having an app with over 1 million downloads in Europe, can offer their apps for direct download from their websites. Apple will still collect a fee from these web downloads, though the exact amount has not been disclosed.
Notarization for iOS Apps
To ensure user security, Apple will implement a notarization process for iOS apps downloaded from websites. This process verifies the app’s authenticity and checks for potential security risks. Developers must commit to ongoing requirements to protect users.
Availability of Alternative App Marketplaces
In addition to web downloads, the DMA mandates that Apple allows third-party app stores on iPhones in the EU. However, these alternative app stores can only offer apps from a single company, limiting their scope.
How this Affects EU Users
These changes will give EU users more freedom in choosing where to download apps for their iPhones. They will no longer be restricted to the App Store, potentially benefiting from a wider selection of apps and competitive pricing.
Eligible Countries and Regions
The new policies will apply to all 27 EU member states, as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway, which are part of the European Economic Area.
Impact on App Marketplace Competition
Potential Benefits for Users
The introduction of alternative app sources could lead to increased competition, potentially resulting in lower app prices, more innovative offerings, and better privacy and security practices from developers vying for users’ attention.
Potential Challenges for Developers
While the changes may benefit users, developers could face challenges. Maintaining multiple distribution channels and complying with different sets of rules and fees could increase development costs. Additionally, the risk of app piracy and unauthorized modifications may rise with web downloads.
Apple’s decision to comply with the DMA’s requirements represents a significant shift in the company’s app distribution strategy. As the new policies roll out, users and developers alike will closely observe the impact on the European app marketplace landscape.