Ever wondered what became of India’s ambitious lunar mission, Chandrayaan 2? The epic journey ended in an unexpected silence when the spacecraft lost communication with the control center during its final descent.
In this insightful article, we’ll delve into what prompted that abrupt ending and how it paves way for the next chapter – Chandrayaan 3. Ready to take a trip through our cosmic neighborhood?
Overview of Chandrayaan 2 Mission
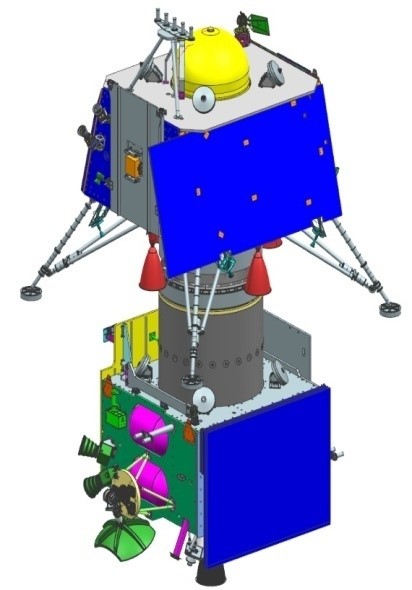
The Chandrayaan 2 mission captured the world’s attention as it aimed to explore the moon’s surface. However, things didn’t go as planned, leaving many wondering what went wrong. In this article, we will delve into the details of Chandrayaan 2 and uncover the reasons behind its failure. By understanding what happened in Chandrayaan 2, we can better grasp the importance of future missions like Chandrayaan 3. Get ready for an adventure that takes us from Earth to space!
Objectives and Goals
The objectives and goals of the Chandrayaan 2 mission were ambitious yet clear. This lunar mission, mounted by India’s space agency, ISRO, aimed for a soft landing on the moon – an achievement that would have marked a significant milestone in lunar surface exploration.
The plan was to study various aspects of the moon’s topography with scientific research equipment onboard. However, despite meticulous planning and preparatory testing, things didn’t go as anticipated.
A sudden technical malfunction led to an unexpected tilt in Vikram Lander during descent causing it to lose contact with ISRO when just 400 meters away from achieving its goal.
Launch and Journey to the Moon
The Chandrayaan 2 mission was a significant step in India’s lunar exploration programs.
- ISRO, the Indian space agency, launched Chandrayaan – 2 on July 22, 2019.
- The aim of the mission was to land a rover on the unexplored South Polar region of the moon.
- The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) carried the spacecraft into Earth’s orbit.
- Following this, an orbiter, lander Vikram, and rover Pragyan began their journey towards the moon.
- They followed a meticulously planned trajectory to save fuel and take advantage of the moon’s gravitational pull.
- After multiple orbit-raising maneuvers around Earth, Chandrayaan-2 headed towards its lunar journey.
- It traveled nearly 384,400 kilometers across space before reaching lunar orbit on August 20, 2019.
- The next critical phase was a soft landing on the lunar surface which has only been achieved by a few countries so far – the United States, China, and Russia.
- The Vikram Lander unexpectedly tilted which caused a change in trajectory and failure to reduce speed as per plan.
- This led to communication loss with the ISRO control center due to a technical glitch and subsequently a hard crash landing occurred on the lunar surface.
- Chandrayaan – 2 managed to capture several detailed images of the Lunar Surface with its orbiter that continues functioning till date giving valuable insights about our nearest celestial neighbor.
- These learnings are now assisting ISRO in preparatory tests for the upcoming Chandrayaan-3 mission – the expected launch date is July 14 at 2:35 PM (IST).
- Their goal remains undeterred – successful Space Exploration including achieving a successful soft landing in future missions using enhanced communication systems and improved navigation techniques learned from previous experiences.
- It marked India’s advanced leap forward in space exploration showcasing the technological prowess of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
Challenges Encountered During the Landing Attempt
The Chandrayaan 2 mission encountered various challenges during its attempted lunar landing, resulting in its ultimate failure to achieve the desired objective.
- The primary issue was a technical glitch that arose unexpectedly during the mission’s most critical phase.
- Accompanied by this glitch, the Vikram lander experienced an unexpected tilt while descending toward the lunar surface.
- This shift in position disrupted the communication with ISRO when Vikram was just 400 meters away from its destination.
- The inability to restore communication led to further complications in navigation during the final descent.
- The trajectory of Vikram changed unexpectedly, making it impossible for ISRO scientists to control its speed and direction.
- Eventually, this resulted in a hard crash landing instead of the intended soft landing on the moon’s surface.
- Such a mishap led to the loss of contact between ISRO and both Vikram, as well as Pragyan, the onboard rover.
- An overlooked software glitch turned out to be a key factor leading to these difficulties.
Reasons for the Chandrayaan 2 Mission Failure
Chandrayaan 2 mission failed due to technical glitches, communication issues with the lander, and navigation difficulties during the final descent.
Technical Glitches and Malfunctions
Chandrayaan-2 encountered several technical glitches and malfunctions, which ultimately led to its mission failure. Here are the key issues that occurred:
- The mission experienced a software glitch during the descent phase, resulting in a loss of contact with ISRO.
- A change in trajectory caused the lander, Vikram, to deviate from its intended path and approach at a higher-than-anticipated angle.
- The lander’s speed reduction maneuver failed, leading to an excessive velocity during the final descent.
- Communication issues arose between the lander and the orbiter, disrupting vital information exchange.
- Despite extensive preparatory tests, some unforeseen technical issues emerged during the mission.
Communication Issues with the Lander
Chandrayaan-2 faced significant challenges in establishing communication with the lander, Vikram. A technical glitch during descent resulted in an unexpected tilt of the lander, leading to a loss of contact with the lunar surface.
This disruption prevented crucial information from being transmitted back to ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization). Efforts have been made to address these issues for Chandrayaan-3, including enhancing communication systems and rectifying software glitches that caused previous failures.
By learning from past mistakes and deploying improved technology, ISRO aims to ensure seamless communication between the spacecraft and ground control during future missions.
Navigation Difficulties During Final Descent
The Chandrayaan-2 mission faced significant navigation difficulties during its final descent, ultimately leading to its failure. As the Vikram lander approached the lunar surface, it encountered unexpected trajectory deviations and struggled to reduce its speed effectively.
These challenges resulted in a change in course and an unsuccessful landing attempt. The failed navigation meant that contact with the lander was lost when it was just 400 meters away from its intended destination.
Scientists and engineers have diligently examined these navigation difficulties to ensure that they are addressed in future missions like Chandrayaan-3. By improving navigation systems and refining landing techniques, ISRO aims to rectify these issues for a successful moon landing in upcoming space exploration efforts.
Lessons Learned and Improvements for Chandrayaan 3
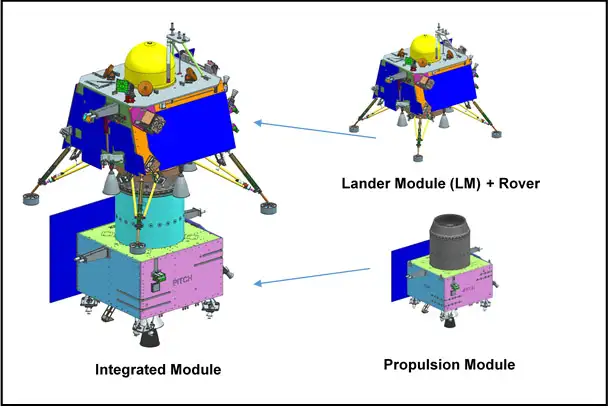
Lessons were learned from the Chandrayaan-2 mission, and improvements have been made for Chandrayaan-3 to avoid similar failures. Enhanced communication systems, improved navigation techniques, and strengthened testing processes are some of the key areas that have been focused on.
Curious to know more? Read on to discover the future of India’s lunar exploration program and what sets Chandrayaan-3 apart from its predecessor.
Enhanced Communication Systems
The failure of Chandrayaan 2’s landing attempt highlighted the crucial need for enhanced communication systems in future lunar missions. To address this, ISRO has meticulously analyzed and rectified the issues faced during Chandrayaan 2, aiming to reduce the risk of losing contact with the lander or experiencing trajectory deviations with Chandrayaan 3.
By improving communication systems, they will significantly enhance their ability to receive vital data and ensure a smoother mission execution. This improvement directly contributes to minimizing potential glitches and maximizing mission success.
Improved Navigation and Landing Techniques
To overcome the challenges faced during the Chandrayaan 2 mission, the upcoming Chandrayaan 3 mission will implement improved navigation and landing techniques. Scientists have meticulously studied the trajectory deviation that occurred during Chandrayaan 2’s descent and have made necessary adjustments to ensure a successful landing on the moon this time around.
Additionally, ISRO has strengthened its testing and quality control processes to minimize any software glitches or technical malfunctions that could disrupt communication with the lunar surface.
These improvements in navigation and landing techniques aim to enhance the precision and accuracy of future lunar missions undertaken by India, marking another milestone in their space exploration endeavors.
Strengthened Testing and Quality Control Processes
To prevent any technical glitches and malfunctions that could jeopardize the success of Chandrayaan 3, ISRO has implemented enhanced testing protocols and quality assurance measures. Here are some improvements made in testing and quality control processes:
- Stringent Pre-launch Preparation: ISRO has intensified its pre-launch preparations by conducting extensive tests on all aspects of the mission, including spacecraft systems, propulsion, communication systems, and payload deployment. This ensures that all components are functioning optimally before launch.
- Thorough Error Rectification: Lessons learned from Chandrayaan-2 have led to improved error rectification procedures. Any potential issues or malfunctions identified during testing are addressed promptly and effectively to minimize the chances of failure during the mission.
- Contact Reliability: Communication is crucial for a successful space mission. To enhance contact reliability between the spacecraft and ground stations, ISRO has upgraded its communication systems with advanced technologies, ensuring seamless communication throughout the mission.
- Trajectory Stability: Achieving a stable trajectory is essential for a successful lunar landing mission. ISRO has employed state-of-the-art navigation techniques to ensure trajectory stability throughout the journey from Earth to the Moon. This includes precise calculations and constant monitoring of the spacecraft’s path.
- Advancements in Space Science: As part of their commitment to innovation, ISRO continuously invests in research and development of new technologies relevant to space exploration. These advancements contribute to improved testing methods and overall quality control processes for future missions like Chandrayaan 3.
Future of the Chandrayaan Space Program
The Chandrayaan space program is set to continue with the upcoming launch of Chandrayaan 3 on July 14, focused on rectifying past mistakes and achieving a successful lunar landing.
Plans for Chandrayaan 3 Mission
Chandrayaan-3, India’s next lunar mission, is set to launch on July 14, 2023. Following the partial failure of Chandrayaan-2 in 2019, this mission aims to learn from past mistakes and achieve a successful soft landing on the moon’s surface.
Unlike its predecessor, Chandrayaan-3 will consist of just a lander and rover. The lander will be equipped with stronger legs for improved stability during landing, and its velocity has been reduced to 2m/second for a smoother touchdown.
Additionally, the mission design places significant emphasis on addressing potential issues that led to previous failures. With expanded landing sites and enhanced communication systems utilizing the orbiter from Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3 marks India’s continued efforts in space exploration and showcases the country’s growing capabilities in this field of endeavor.
Launch Date and Time of Chandrayaan 3
Chandrayaan-3, the next mission in India’s ambitious space program, is all set to launch on July 14 at 2.35 PM (IST). This highly anticipated mission aims to rectify the mistakes made during Chandrayaan-2 and achieve a successful landing on the moon.
With preparatory tests already conducted to avoid repeating past errors, this launch holds great significance for India’s space exploration efforts. The focus of Chandrayaan-3 will primarily be on other aspects of lunar exploration, contributing to scientific research and advancements in the field of space exploration.
As the countdown begins, scientists and space enthusiasts from around the world eagerly await this important step toward achieving India’s goals in lunar exploration.
Difference Between Chandrayaan 2 and Chandrayaan 3
The differences between Chandrayaan 2 and Chandrayaan 3 are numerous, reflecting the lessons learned from the previous mission and the advancements made in space exploration.
| Features | Chandrayaan 2 | Chandrayaan 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Launch Date | July 22, 2019 | July 14, 2023 |
| Launch Time | 02:43 PM | 02:35 PM |
| Launch Vehicle | GSLV Mark III M1 | LVM3 M4 |
| Payload Mass | 3,877 kg | 3,900 kg |
| Rover | Pragyan | Pragyan |
| Special Payload | Not present | SHAPE for conducting measurements |
| Main Focus | Lunar exploration | Rectifying previous mission mistakes |
| Communication System | Encountered issues during descent | Enhanced to prevent past failures |
| Lander Design | Standard legs | Strengthened legs |
| Orbiter Use | Launched with mission | Utilizing orbiter from Chandrayaan 2 |
| Mission Design | Standard | Failure-based, focusing on addressing potential issues |
This table demonstrates the thorough planning and adjustments made for Chandrayaan 3, reflecting India’s continued dedication to their space program and to scientific advancements in the field of space exploration.


